Repeatability:±0.005/0.01mmHorizontal Load:150kgVertical Load:55kgMaximum Speed:2000mm/sTravel Range:100-1500mm
 Current location:Home > Company > News > Latest news > Ball Screw Linear Actuator vs Belt Actuator: Which Is Better for Your Application?
Current location:Home > Company > News > Latest news > Ball Screw Linear Actuator vs Belt Actuator: Which Is Better for Your Application? Date: Nov 18 2025
Linear actuators are fundamental components in modern automation and industrial machinery. Whether used in semiconductor handling, LCD inspection, PCB assembly, medical devices, or automated testing systems, actuators serve as the backbone of precise linear movement. Among the many transmission methods available, ball screw linear actuators and belt actuators are two of the most widely used options.
Each method provides its own set of advantages, performance characteristics, and limitations. Choosing between the two depends on a thoughtful understanding of speed, precision, load requirements, environmental conditions, and structural design.
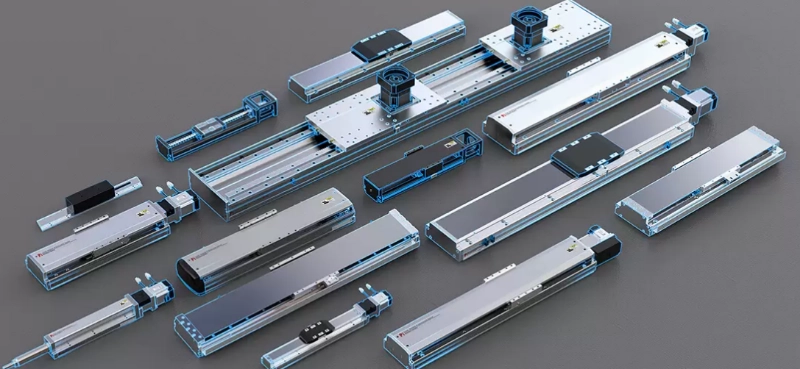
At Ruan Pi-Robot, a company established in 2003 with a commitment to improving industrial precision, both technologies are core components of the product portfolio. With 20 years of accumulated experience and two industrial parks totaling 70,000 square meters in Shenzhen and Yueyang, the company provides a complete range of motion solutions, including precision positioning slide tables, XY linear slide tables, electric cylinders, rectangular coordinate modules, linear motor modules, built-in slide tables, industrial robot arms, and automatic transmission components.
This article compares ball screw linear actuators and belt actuators to help engineers, integrators, and automation professionals identify which solution best meets their requirements.
Ball screw actuators convert rotary motion into linear travel through a ball screw and nut assembly. Recirculating ball bearings reduce friction while maintaining rigidity and precision.
High precision and repeatability: Suitable for tasks requiring controlled, micron-level movement.
Strong load-bearing capability: The screw structure carries heavier loads than other mechanical options of similar size.
Predictable and stable motion: Ideal for precision processes that require accuracy during continuous duty cycles.
Higher rigidity: Ensures minimal deflection and consistent positioning.
Semiconductor wafer handling
Precision dispensing systems
Medical analyzers
CNC auxiliary axes
Optical inspection
Automated assembly platforms
High-accuracy testing equipment
Ball screw technology is typically selected when accuracy and load requirements outweigh the need for maximum speed or extremely long stroke lengths.
Belt actuators use a reinforced timing belt and pulley system to drive a carriage along a linear guide. The design enables long travel distances and high-speed operation.
Very high speed capability: Belt systems often reach faster velocities than ball screw actuators.
Long stroke lengths: Ideal for applications requiring extended travel beyond what typical screw actuators offer.
Low noise and smooth motion: Beneficial for equipment that demands quiet operation.
Lower inertia: Allows for rapid acceleration and deceleration.
High-speed pick-and-place
Packaging machinery
Material transfer modules
Light-duty assembly lines
Long travel automation systems
Rapid inspection and scanning
If the priority is speed or stroke length rather than micron-level precision, a belt actuator is often the better choice.
Ball Screw:
Offers superior accuracy and repeatability, making it the preferred choice for semiconductor tools, laboratory systems, and high-precision inspection.
Belt:
Provides general-purpose accuracy suitable for many industrial tasks but not ideal for applications where tolerance levels must remain extremely tight.
Best for Precision:
Ball screw linear actuator
Ball Screw:
Moderate to high speed, depending on screw pitch and motor selection. Not suitable for extreme high-speed applications due to mechanical limitations.
Belt:
Among mechanical actuators, belt systems provide the fastest travel speeds and quick acceleration.
Best for Speed:
Belt actuator
Ball Screw:
Handles heavier loads with minimal deformation due to the screw shaft’s rigidity.
Belt:
Designed for light to medium loads; not ideal for heavy-duty vertical positioning or high-force applications.
Best for Load Capacity:
Ball screw actuator
Ball Screw:
Limited by screw deflection and critical speed. Extended lengths require larger diameters or special support mechanisms.
Belt:
Easily supports long stroke lengths, making it suitable for material transfer or wide-area scanning.
Best for Long Travel:
Belt actuator
Ball Screw:
Requires periodic lubrication and inspection, especially in applications with high loads or continuous cycling.
Belt:
Belts may require tension adjustments or replacement depending on usage but generally offer good long-term durability.
Best for Low Maintenance:
Depends on operating conditions.
For clean environments → Belt
For controlled accuracy → Ball Screw
Both technologies are cost-effective when properly matched to the application.
Ball screw actuators cost more to manufacture but provide long-term accuracy. Belt actuators are simpler and easier to integrate into modular automation systems.
When selecting, engineers should consider lifecycle performance rather than focusing solely on component-level cost.
The best actuator depends on the performance requirements of the equipment:
High precision and repeatability
Strong load capacity
Vertical or force-critical positioning
Controlled, stable movement
CNC-level rigidity
Smooth micro-movement
Accuracy over long cycles
Fast travel speed
Long stroke length
Lower inertia
Quiet running conditions
High throughput scanning or handling
A cost-efficient general-purpose actuator
For many automation platforms, combining different actuator types within the same system delivers the best balance of speed and accuracy.
Ruan Pi-Robot provides a complete selection of both technologies through its precision actuator product range, allowing engineers to choose the model that best matches their motion requirements.
With expertise built over two decades, Ruan helps customers select actuators through:
Structural design analysis
Load calculation and selection
Motor matching and tuning
Environmental requirement evaluation
Multi-axis system layout
Custom actuator options
Industries served include semiconductor new energy, LCD manufacturing, PCB processing, medical automation, automotive electronics, and specialized testing equipment. Each application demands different motion characteristics, and Ruan’s engineering team ensures that the selected actuator aligns with the performance targets.
Both ball screw linear actuators and belt actuators play important roles in automation. The correct choice depends on motion precision, load, stroke length, speed, and environmental factors. Ball screw actuators excel in precision and rigidity, while belt actuators dominate in speed and long travel.
Ruan Pi-Robot continues to support global automation customers with advanced actuator solutions grounded in real engineering practice. From design to production, the company remains committed to helping industries achieve higher levels of accuracy, reliability, and efficiency.