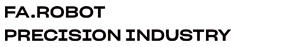Repeatability:±0.005/0.01mmHorizontal Load:150kgVertical Load:55kgMaximum Speed:2000mm/sTravel Range:100-1500mm
 Current location:Home > Company > News > Latest news > How to Evaluate the Load Capacity of a Precision Positioning Slide Table
Current location:Home > Company > News > Latest news > How to Evaluate the Load Capacity of a Precision Positioning Slide Table Date: Feb 04 2026
When selecting a precision positioning slide table for your project, one of the most important specifications to evaluate is its load capacity. The load capacity determines the maximum weight the slide table can handle while still maintaining precision, stability, and operational efficiency. Choosing the right load capacity for your application ensures that the slide table will perform reliably over time without compromising its accuracy or durability.
In this article, we’ll guide you through the key factors to consider when evaluating the load capacity of a precision positioning slide table. We’ll break down the different types of loads and how to assess the right specifications to suit your project’s needs.
Before diving into the details of load capacity, it's essential to distinguish between static and dynamic load.
Static Load: This refers to the weight that the slide table can carry when it is stationary. Static load capacity is usually higher because there’s no movement involved, and the table is simply supporting the weight.
Dynamic Load: This is the weight the table can support while in motion. When the table moves, there are additional forces at play, such as inertia and acceleration, which can reduce the table's effective load capacity.
What to do: Make sure to assess both static and dynamic load requirements based on your application. For instance, if you’re moving heavy parts or machinery that require frequent adjustments, dynamic load capacity is critical. If the table is primarily used for holding static components, static load capacity might be more important.
The next step is to calculate the maximum load the slide table will need to support in your specific application. This includes:
The weight of the components you plan to move or position.
Additional forces that may be applied during the motion, including acceleration, deceleration, and vibration.
It’s essential to account for these factors to avoid overloading the slide table and ensure that it performs optimally.
What to do:
Estimate the weight of each object you plan to move, along with any attachments, tools, or fixtures that will be added to the table.
Consider extra weight that may be added during operation, such as tools or workpieces that could be mounted on the slide table.
If your system involves acceleration or deceleration, calculate the forces involved. For example, heavier components may experience more stress during high-speed movements.
Every precision positioning slide table comes with manufacturer-provided load ratings that indicate the maximum static and dynamic load the system can handle. These ratings are determined based on extensive testing and engineering specifications.
However, just looking at the load ratings isn’t enough. It’s essential to understand how the manufacturer defines these values and whether they match your specific needs.
What to do:
Review the load capacity specified by the manufacturer and ensure it aligns with your calculated load requirements.
Understand the application context: For example, some tables may perform well under light, steady loads but may not be suitable for heavy-duty, high-speed applications.
Look for additional information like safety factors or any limitations on load capacity, such as the distance over which the load can be moved.
The design and materials used in the construction of the precision positioning slide table directly affect its load capacity. A more robust design with high-strength materials will allow the table to support greater weights without compromising performance.
Common materials used for slide tables include:
Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, but may not support very heavy loads.
Steel: Stronger and more durable, making it ideal for higher load capacities, but heavier than aluminum.
Stainless Steel: Offers both strength and corrosion resistance, suitable for demanding environments.
Ceramics or Composite Materials: Used in applications where minimal weight is required but high rigidity is essential.
What to do:
Evaluate the materials: For high-load applications, look for tables made of stronger, more rigid materials like steel or stainless steel.
Assess the design: A well-engineered slide table with reinforced structures and optimized support mechanisms will better distribute weight and prevent distortion under heavy loads.
The way the load is distributed on the slide table can have a significant impact on the overall performance. Uneven or concentrated loads may cause issues like bending, misalignment, or damage to the rails and bearings.
Even load distribution: Ensures the slide table moves smoothly and maintains its precision.
Concentrated load: Can result in excessive wear on one part of the system, leading to imbalances and inaccuracies.
What to do:
Ensure even weight distribution across the surface of the slide table.
If your load is concentrated in one area, consider using additional support structures or mounting solutions to balance the load and reduce stress on the table.
The load capacity is often tied to the travel distance of the slide table. For example, a table may be able to support a higher static load but may lose some of that capacity over longer travel distances, especially if the load is at one end.
The force applied during movement, such as acceleration or jerk, can also impact the load capacity. The longer the travel distance, the more dynamic forces may affect the slide table’s performance.
What to do:
Evaluate the distance over which the slide table needs to travel and ensure that the load is within the capacity for that range of motion.
Consider the nature of motion: Frequent starts, stops, or high-speed movements will impact the load-bearing capacity, especially at the extremes of the travel range.
Load-bearing components, such as rails, bearings, and guide systems, wear out over time, especially when subjected to heavy loads. It’s important to consider the maintenance requirements and the longevity of the slide table when selecting a model.
Mistake: Ignoring the long-term effects of heavy loads on the slide table.
What to do: Look for slide tables with self-lubricating systems or sealed bearings to reduce wear from high loads. Regular maintenance, such as lubrication and cleaning, will also extend the life of the slide table.
When selecting a precision positioning slide table, understanding how to evaluate its load capacity is essential for ensuring reliable performance and preventing premature failure. By considering factors like static and dynamic loads, material strength, load distribution, and maintenance needs, you can select a slide table that meets your specific application requirements.
Taking the time to carefully assess your load requirements and match them with the appropriate slide table will save you time, reduce operational risks, and enhance the overall efficiency of your system. Whether you’re dealing with light components or heavy-duty industrial tasks, making the right choice in load capacity is crucial to your success.